Background:Artificial intelligence (AI) promises to revolutionize hematology care.Patients undergoing inpatient allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) often experience psychological consequences, some of which may be attributed to anxiety about how to optimally care for themselves when returning home.Care.coach Avatar TM is a tablet-based ‘human-in-the-loop’ virtual health assistant (VHA) that utilizes generative AI and deterministic software to provide psychosocial support and health coaching to inpatients. It has been shown to improve loneliness, depression, anxiety, hospital delirium, and falls in older adults in the hospital (Chi, Geriatr Nurs 2017; Bott, J Med Internet Res 2019).
Methods: We adapted the care.coach Avatar TM VHA for inpatient HCT, designing an education program to prepare patients for safe return to the home setting. The VHA engages patients with reminders for hydration, medications, food, or activity; education modules adapted for HCT; playing games such as jeopardy, chess, blackjack, trivia, or bingo; playing the news or music; having free-form conversations; going through therapeutic activities and exercises; and practicing mindfulness and guided meditation. Avatar protocols were updated based on feedback from a structured focus group (n=10) of nurse navigators, inpatient HCT nurses, and HCT physicians at the Dana-Farber/Harvard Cancer Center that was convened to discuss perspectives on implementation of care.coach Avatar TM VHA for HCT. Seven HCT-specific educational modules were created. A feasibility pilot was then performed in 3 sequential cohorts of 6 patients receiving reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) HCT. In the first cohort, patients were given the VHAs without any recommendations for how long to use them. The second cohort was given a recommendation for 30 minutes per day, and the third cohort was offered a $20 gift card for completion of at least 4 modules. Responses were measured through patient surveys and engagement data analysis. The predefined retention rate for feasibility was 67%, a standard for introduction of a novel AI technology (Teresi, Med Care 2022). Dissatisfaction rate for the overall VHA experience was defined as responding “disagree” or “strongly disagree” with recommending the VHA to others.
Results: The study included 18 patients, with a majority female (61%) and white (72%; Table). The median age of the patients was 63 (interquartile range [IQR] 56-66). The retention rate from enrollment to discharge or three weeks (whichever came first) was 78% (95% exact confidence interval: 52-94%). The median length of use was 9 days (IQR 6-11). A post-pilot survey was completed by 16 patients (90%), revealing a dissatisfaction rate of 28%. The dissatisfaction rates decreased from 50% to 20% to 0% across the 3 cohorts. Frequency of completion of the post-pilot survey for the full study was 72% within 1 week of disenrollment, and 90% overall. Average completion rate was 52% for all seven HCT modules in the whole study population. Across cohorts, module completion rates changed from 5% to 88% to 62%, reflecting evolving guidance to patients at study initiation.
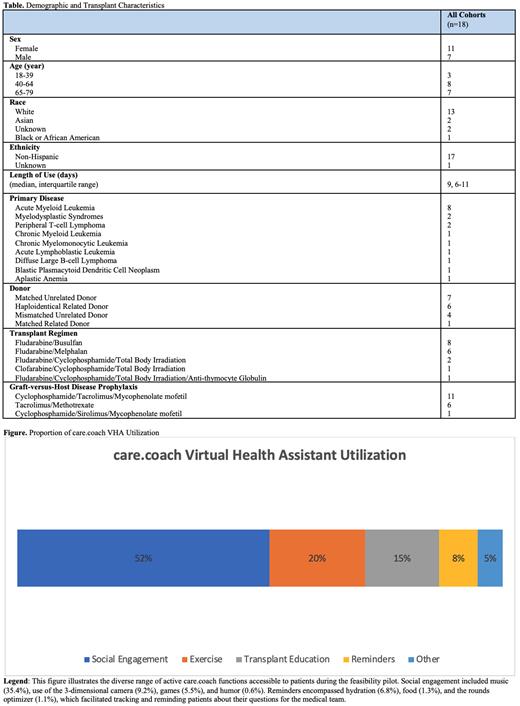
The median average daily interaction time with the avatar for all 18 patients was 28 minutes with an interquartile range from 20 to 38 minutes. The most frequently used VHA functions by time of usage were music (35%), exercise (20%), and education (15%; Figure). The least frequently used VHA functions were the rounds optimizer (a tool to remind patients of their questions during rounds; 1%) and humor (1%). Overall, 52% of time using the VHA was spent on social engagement activities.
Conclusions: The pilot study demonstrated the feasibility of implementing the care.coach Avatar TM VHA for inpatient HCT patients. Despite modest dissatisfaction and variability in completion rates, the VHA showed promise in providing HCT education, social, and emotional support for inpatient RIC HCT. Further research is needed to assess the impact of this novel technologic intervention on HCT outcomes and quality of life, as well as application to the outpatient HCT setting.
Disclosures
Kelkar:CareDx: Research Funding. Kerssens:Care.coach Corporation: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Cutler:Sanofi: Consultancy; Allovir: Other: Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB); Pluristem Therapeutics: Other: DSMB; Ruth L. Kirschstein Postdoctoral Individual National Research Service Award: Research Funding; InhibRx: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; Rigel: Consultancy; Oxford Immune Algorithmics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cimeio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Sherman-Manhard:Care.coach Corporation: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Soiffer:NMPD - Be the Match, USA: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Juno Therapeutics/ BMS/Celgene USA: Other: Data Safety Monitoring Board; Jasper: Consultancy; Bluesphere Bio: Consultancy; Smart Immune: Consultancy; Neovii: Consultancy; Vor Bipharma: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy. Wang:Care.coach Corporation: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal